Explore how melting glaciers reveal the accelerating impact of global warming and its worldwide environmental consequences.
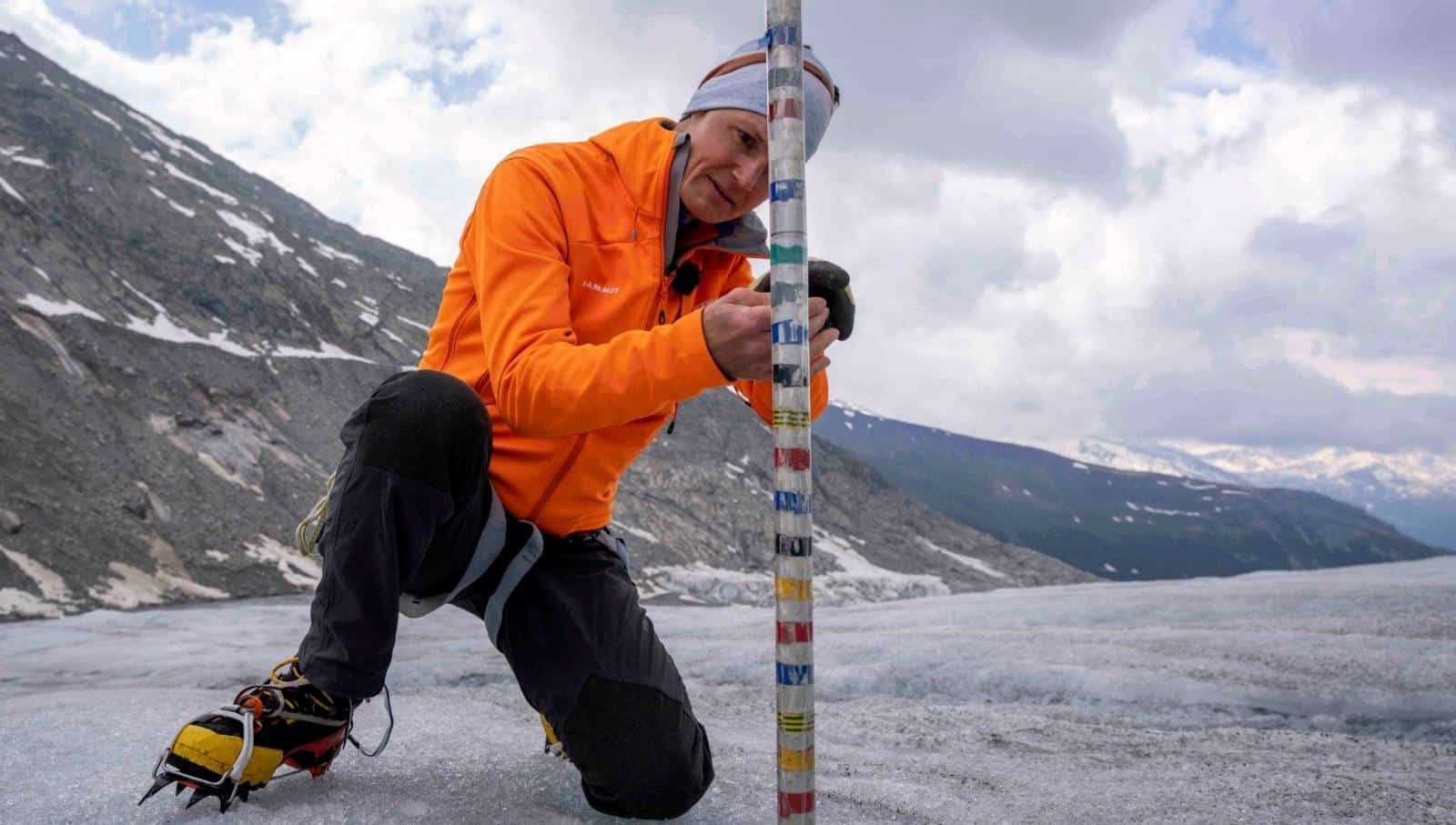


Recent scientific observations reveal that the consequences of global warming are becoming increasingly severe. Rising temperatures are leading to the rapid reduction of ice masses across the globe. Experts project that by the end of this century, glaciers in regions such as the European Alps and the Caucasus Mountains may completely vanish.
According to data from NASA, both the atmosphere and oceans are warming, accelerating the melting of glaciers that serve as vital freshwater reserves. Antarctica alone loses about 135 billion tons of ice annually, while Greenland’s loss is approximately twice that figure. These dramatic transformations underscore how quickly the Earth’s climate system is shifting.
Sayfa İçerikleri
ToggleDr. Matthias Huss, a leading researcher from the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich, explains that glacier recession is primarily linked to evolving climatic conditions. He emphasizes that the temperature increases of the past century are largely a result of human activity, particularly industrial emissions and deforestation.
Between 2010 and 2020, the overall rate of glacier melting rose by nearly 36% compared to the previous decade. Small and mid-sized glacier systems, such as those in the European Alps, the Rocky Mountains, and the Caucasus, are showing the most rapid declines. Meanwhile, extensive ice masses like those in Alaska and Patagonia are experiencing significant losses in total volume.
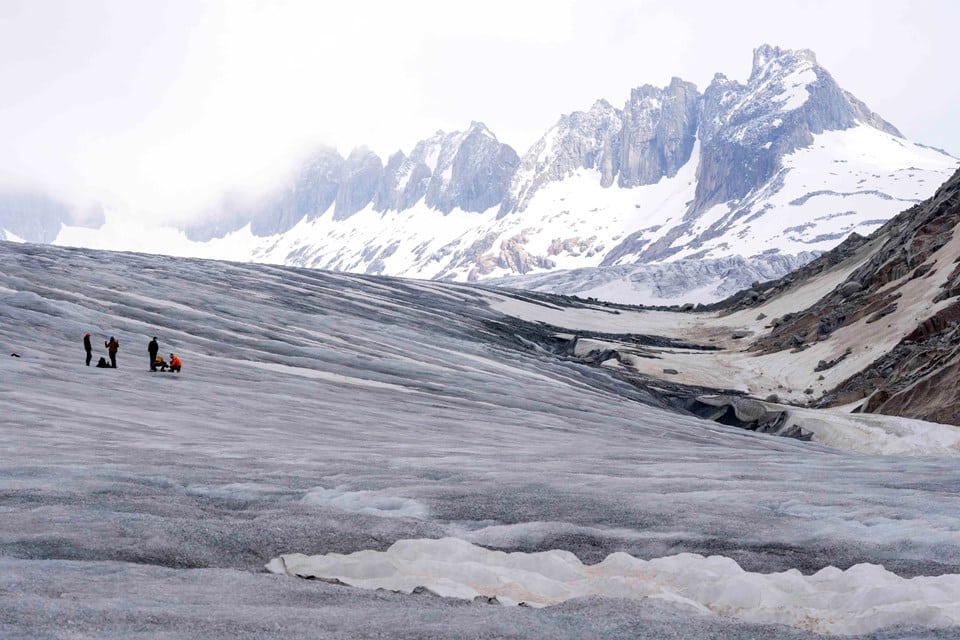

Researchers warn that if warming trends continue, the retreat of glaciers will intensify. Predictions indicate that between 26% and 41% of existing glaciers could disappear by 2100. In some regional models, nearly every glacier in the European Alps and Caucasus Mountains is expected to melt completely under high-emission scenarios.
The repercussions extend well beyond the loss of scenic ice landscapes. Sea-level rise remains the most significant concern, with expectations of at least a one-meter increase by the end of the century. This escalation would place coastal populations and ecosystems at severe risk, threatening billions of lives and livelihoods.
In addition to flooding risks, glacier melt alters the balance of marine ecosystems by changing sediment flow and nutrient distribution near coastal areas. These changes could have lasting impacts on ocean biodiversity and local economies dependent on these environments.
Experts stress that the only realistic path to preserving the remaining glaciers lies in drastically reducing carbon emissions. Limiting the global temperature rise through sustainable environmental policies and alternative energy use can slow down the process of melting and safeguard future generations from the direst climate outcomes.
Every fraction of a degree matters. The world stands at a pivotal moment, and collective efforts to mitigate climate change can determine whether the Earth’s frozen reservoirs will survive the coming century.


























Sigortahaber.com, sigorta sektöründeki en güncel haberleri, analizleri ve gelişmeleri tarafsız bir bakış açısıyla sunan bağımsız bir haber platformudur. Sigorta profesyonellerine, acentelere ve sektöre ilgi duyan herkese doğru, hızlı ve güvenilir bilgi sağlamayı amaçlıyoruz. Sigortacılıktaki yenilikleri, mevzuat değişikliklerini ve sektör trendlerini yakından takip ederek, okuyucularımıza kapsamlı bir bilgi kaynağı sunuyoruz.
Yorum Yap