

Have you ever noticed the ‘Fast Boot’ option while navigating through your computer’s BIOS (Basic Input/Output System)? Fast Boot is a handy feature that accelerates your computer’s startup process by bypassing some of the usual boot steps.

Who doesn’t want their system to spring to life faster? This feature can be a time-saver if you’re eager to get working or gaming swiftly, but it does come with its own set of caveats. In this article, we will delve into the details and help you decide whether to enable it or not.
Fast Boot, specifically available in UEFI-enabled systems and Windows 8 onwards, transforms a typical shutdown into a sort of ‘deep hibernation’. Instead of turning off completely, crucial start-up files are stored in a hibernation file, allowing a quicker boot when the system powers back on.
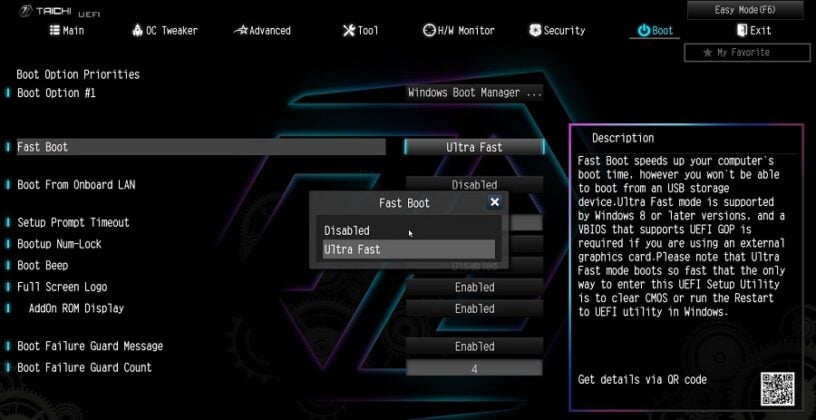
This feature optimizes boot time by storing configuration and hardware data in a special memory area. As a result, during shutdown, the system enters a hybrid state, making it quicker to resume operations when restarted.
The primary benefit of enabling Fast Boot is significantly reduced boot times, which can sometimes be halved. If you’re frequently using your PC, this can be a real time-saver, allowing you to dive into tasks or gaming more swiftly. It can also aid in energy conservation, as the system doesn’t fully shut down and consumes less power.
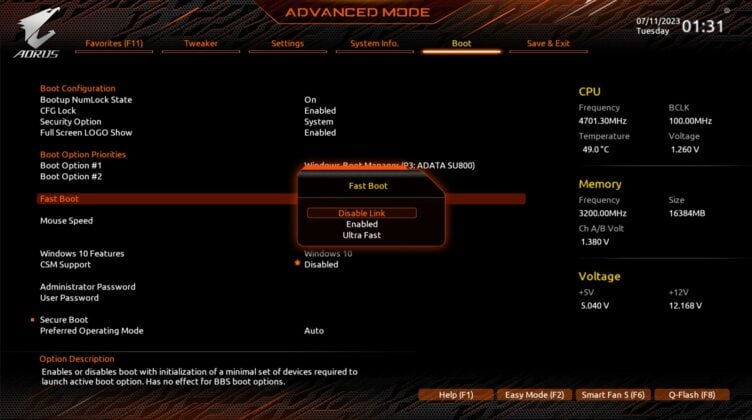
System Instability: While enabling Fast Boot itself may not be problematic, it can exacerbate existing issues. For instance, a crash with Fast Boot activated might corrupt the hibernation file, potentially resulting in boot loops or system instability.
Hardware Changes: If you’re upgrading hardware, like installing more RAM, you might need to disable Fast Boot temporarily to ensure the system recognizes the changes.
Compatibility Issues: Systems with multiple boot drives or dual operating systems might face challenges, as Fast Boot is primarily designed for single Windows installations.
Device Detection: Fast Boot may skip some BIOS checks, potentially missing new hardware or updated drivers, leading to errors or missing functionalities.
To toggle Fast Boot on or off, you need to access the BIOS settings. This option usually resides under the ‘Boot’ or ‘Advanced’ tab. Simply navigate to it, press Enter, and use the arrow keys to select ‘Enable’ or ‘Disable’. Some BIOS versions even offer different levels of Fast Boot, such as normal, fast, or ultra-fast.

Different manufacturers use different hotkeys for BIOS access. Here’s a quick reference list:
By pressing these keys during startup, you should access the BIOS screen. If you’re uncertain, consult the manual or visit the manufacturer’s website for precise instructions.
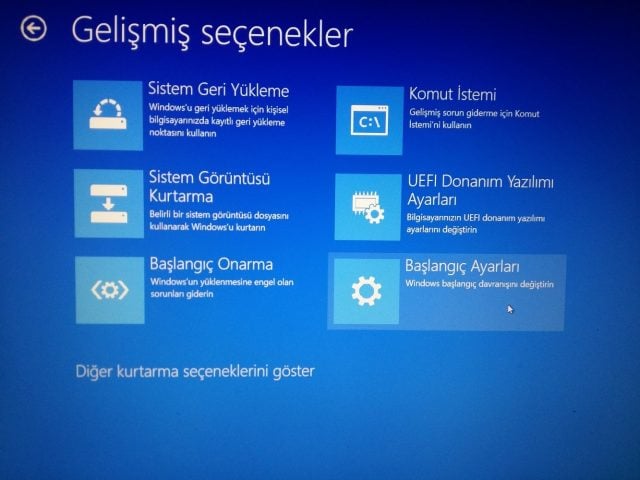
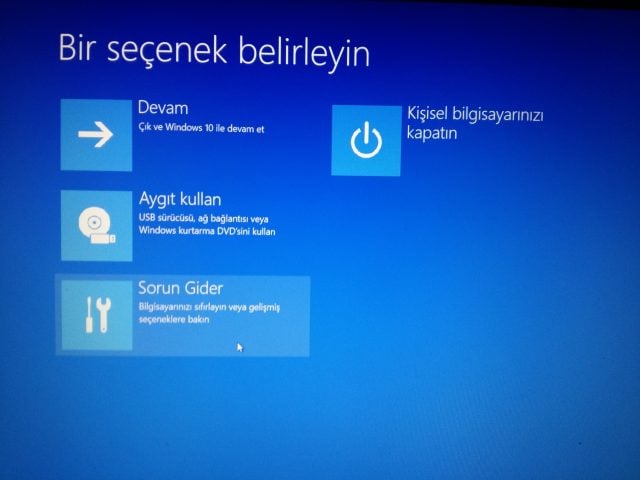
Modern computers boot quickly, which can make accessing the BIOS tricky. Here’s an alternative method:
After restarting, choose Troubleshoot, then Advanced options, and finally, ‘UEFI Firmware Settings’. This will reboot your system into the BIOS, allowing you to disable Fast Boot if needed.
Fast Boot is a convenient feature, but it requires understanding its implications. With this guide, you’re now equipped to make an informed decision about using it on your system.
SİGORTA
2 gün önceSİGORTA
2 gün önceBLOG
2 gün önceBLOG
2 gün önceBLOG
2 gün önceBLOG
2 gün önceBLOG
2 gün önceBLOG
2 gün önceBLOG
2 gün önceBLOG
2 gün önce 1
DJI Mini 5: A Leap Forward in Drone Technology
18696 kez okundu
1
DJI Mini 5: A Leap Forward in Drone Technology
18696 kez okundu
 2
xAI’s Grok Chatbot Introduces Memory Feature to Rival ChatGPT and Google Gemini
13955 kez okundu
2
xAI’s Grok Chatbot Introduces Memory Feature to Rival ChatGPT and Google Gemini
13955 kez okundu
 3
7 Essential Foods for Optimal Brain Health
12864 kez okundu
3
7 Essential Foods for Optimal Brain Health
12864 kez okundu
 4
Elon Musk’s Father: “Admiring Putin is Only Natural”
12706 kez okundu
4
Elon Musk’s Father: “Admiring Putin is Only Natural”
12706 kez okundu
 5
Minnesota’s Proposed Lifeline Auto Insurance Program
10605 kez okundu
5
Minnesota’s Proposed Lifeline Auto Insurance Program
10605 kez okundu
Veri politikasındaki amaçlarla sınırlı ve mevzuata uygun şekilde çerez konumlandırmaktayız. Detaylar için veri politikamızı inceleyebilirsiniz.
Sigorta Güncel Sigorta Şikayet Güvence Haber Hasar Onarım Insurance News Ajans Sigorta Sigorta Kampanya Sigorta Ajansı Sigorta Sondakika Insurance News