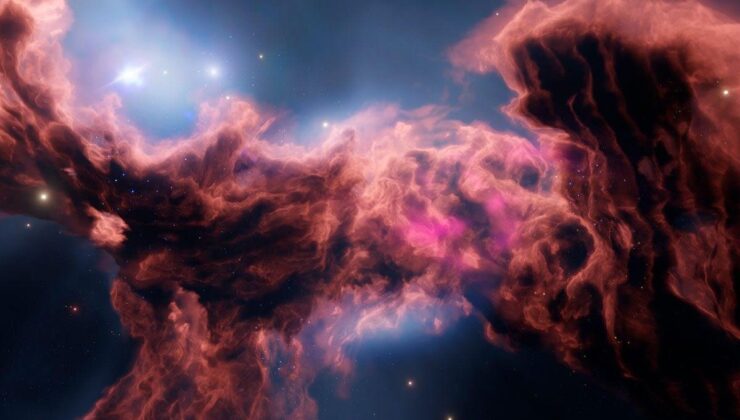


The realm of astronomy has unveiled an astonishing discovery, shedding light on molecular clouds—often revered as the cradles of stars. Researchers have identified a colossal hydrogen cloud a mere 300 light-years from the Solar System. This structure, named Eos after the Greek goddess of dawn, represents a significant leap forward. Notably, it is the first cloud found directly through the far-ultraviolet radiation of molecular hydrogen.
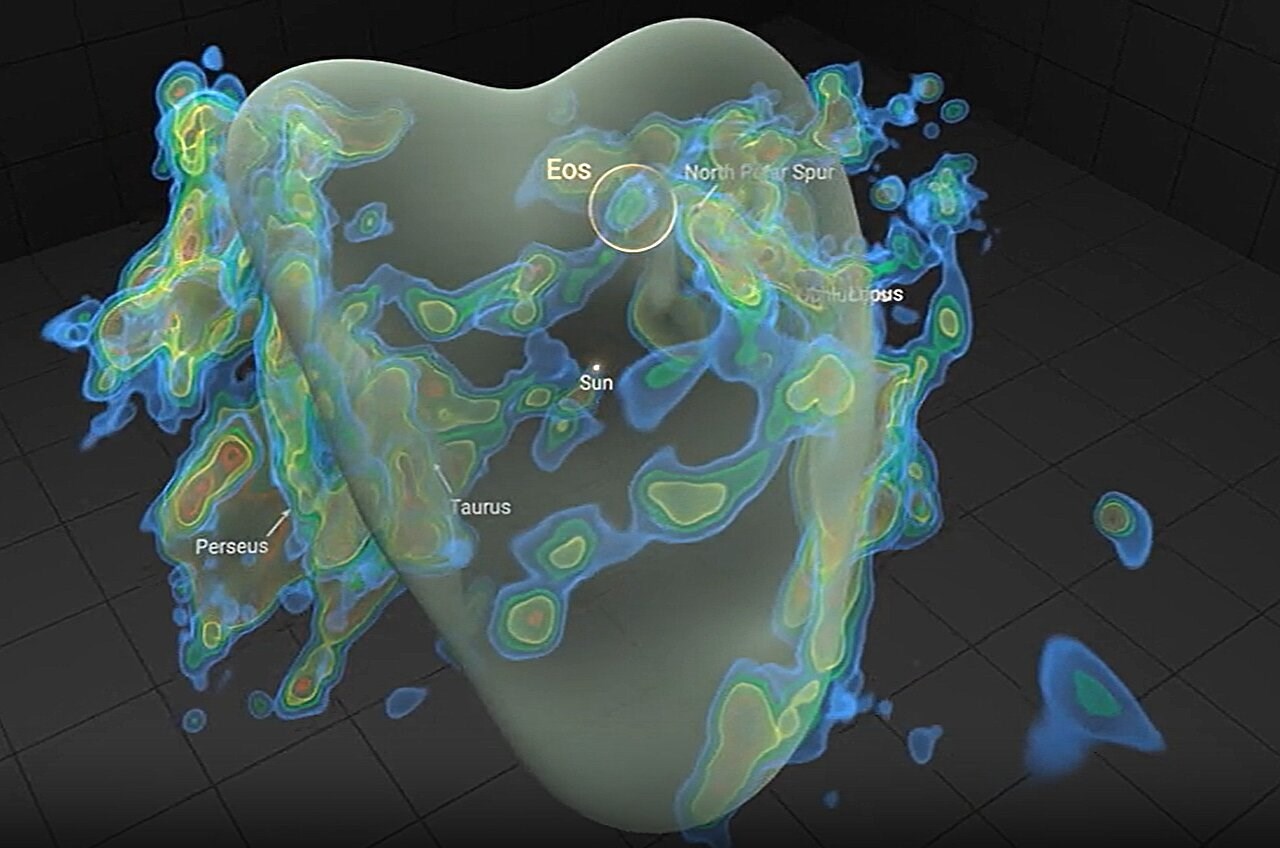
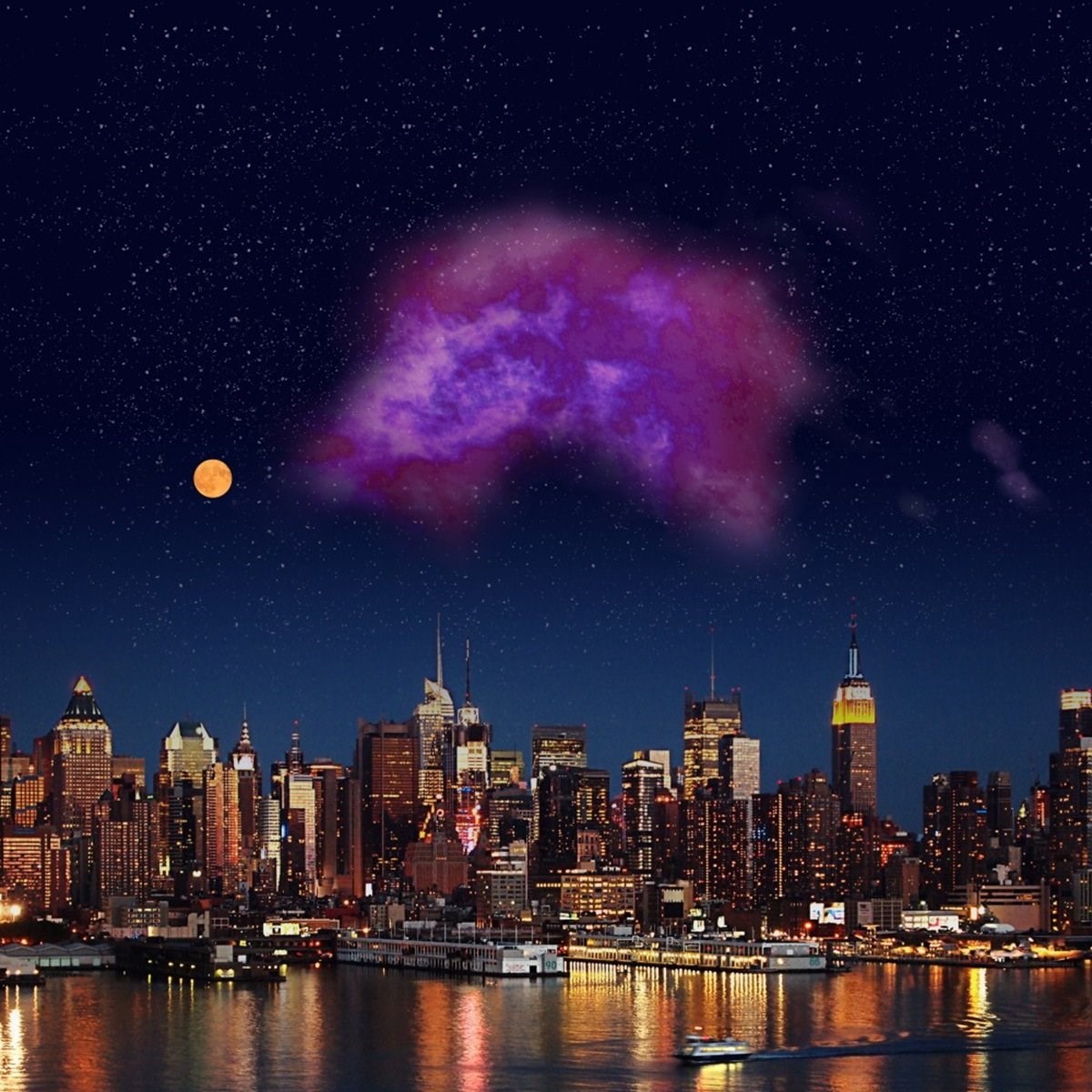
Covering an expanse in the sky equivalent to 40 full moons, Eos boasts a mass approximately 3,400 times that of the Sun. This massive structure offers a unique window into the star formation processes within the Milky Way. Molecular clouds, comprised of gas and dust, host hydrogen as their primary molecule—the fundamental building block for stars, planets, and life itself. These clouds also house other molecules like carbon monoxide.

Traditionally, molecular clouds were discovered through radio and infrared observations that detect carbon monoxide. However, the team led by Blakesley Burkhart, a professor of physics and astronomy at Rutgers University, adopted an unconventional approach. While normally detected by studying dust emissions, Eos was discovered based on radiation emitted by hydrogen in the far-ultraviolet spectrum. This wavelength, challenging to observe due to atmospheric absorption, is now accessible thanks to space-based instruments.
Data for this study was sourced from a spectrograph aboard the Korean satellite STSAT-1. Eos resides on the outskirts of a hot plasma region known as the “Local Bubble”, the cosmic neighborhood of our Solar System. Scientists are eager to exploit Eos’ proximity to gain insights into stellar and planetary formation processes within this region. Such a nearby and expansive molecular cloud provides an unparalleled opportunity for detailed observation.
Experts anticipate that Eos’ discovery is just the beginning. The novel method employed could lead to the identification of other “invisible” molecular clouds across the Milky Way, further enriching our understanding of the cosmos.
BİLGİ
Az önceBİLGİ
Az önceSİGORTA
8 saat önceSİGORTA
1 gün önceSİGORTA
1 gün önceSİGORTA
3 gün önceINSURANCE NEWS
3 gün önceSİGORTA
5 gün önceSİGORTA
5 gün önceSİGORTA
5 gün önce 1
DJI Mini 5: A Leap Forward in Drone Technology
20588 kez okundu
1
DJI Mini 5: A Leap Forward in Drone Technology
20588 kez okundu
 2
xAI’s Grok Chatbot Introduces Memory Feature to Rival ChatGPT and Google Gemini
14555 kez okundu
2
xAI’s Grok Chatbot Introduces Memory Feature to Rival ChatGPT and Google Gemini
14555 kez okundu
 3
7 Essential Foods for Optimal Brain Health
13279 kez okundu
3
7 Essential Foods for Optimal Brain Health
13279 kez okundu
 4
Elon Musk’s Father: “Admiring Putin is Only Natural”
13114 kez okundu
4
Elon Musk’s Father: “Admiring Putin is Only Natural”
13114 kez okundu
 5
Minnesota’s Proposed Lifeline Auto Insurance Program
11017 kez okundu
5
Minnesota’s Proposed Lifeline Auto Insurance Program
11017 kez okundu
Sigorta Güncel Sigorta Şikayet Güvence Haber Hasar Onarım Insurance News Ajans Sigorta Sigorta Kampanya Sigorta Ajansı Sigorta Sondakika Insurance News