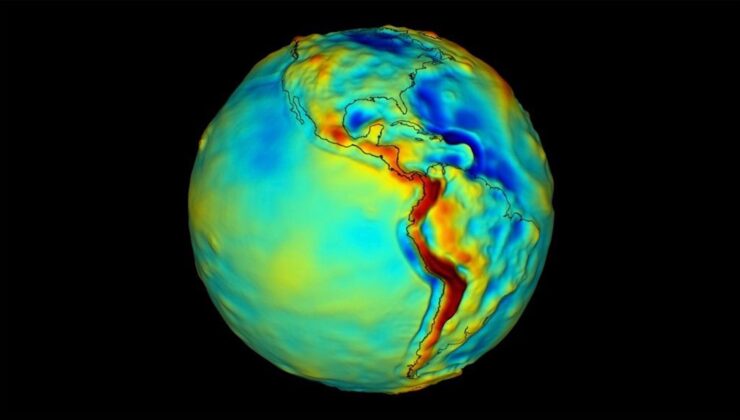

NASA is at the forefront of innovation with its groundbreaking development of a space-based quantum sensor designed to detect the most minute tremors in Earth’s gravitational field. This pioneering technology is set to offer unprecedented insights into the planet’s subterranean architecture by accurately measuring subtle changes beneath the Earth’s surface, including water flows, tectonic shifts, and geological displacements.

Under the expert guidance of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), the sensor, aptly named the “Quantum Gravity Gradiometer Pathfinder” (QGGPf), boasts the capability to identify underground features such as aquifers and mineral deposits. Such data is invaluable not just for scientific exploration but also for applications in navigation, resource management, and national defense. In a statement, Jason Hyon, director of JPL’s Quantum Space Innovation Center, expressed, “We can determine the mass of the Himalayas using atoms.”
Unlike traditional mechanical systems, the QGGPf sensor employs clouds of atoms chilled to near absolute zero. When released into free fall, these atoms are targeted with laser beams, which separate and then recombine them. The resulting interference patterns reveal how gravity affects the atoms, allowing scientists to detect even the slightest gravitational variations. This innovative method, known as “atom interferometry,” delivers significantly more precise outcomes compared to conventional techniques.
A remarkable feature of the QGGPf sensor is its compact form. With dimensions akin to a small washing machine and weighing approximately 125 kilograms, it is remarkably smaller and lighter than traditional gravity measurement tools. NASA intends to launch this cutting-edge sensor into orbit by the late 2020s. This inaugural space mission will not only validate the QGGPf’s capabilities but will also yield crucial insights into the functionality of quantum technologies in the space environment.
SİGORTA
16 saat önceSİGORTA
17 saat önceSİGORTA
17 saat önceSİGORTA
17 saat önceSİGORTA
17 saat önceSİGORTA
17 saat önceINSURANCE NEWS
5 gün önceSİGORTA
5 gün önceSİGORTA
8 gün önceSİGORTA
8 gün önce 1
DJI Mini 5: A Leap Forward in Drone Technology
20481 kez okundu
1
DJI Mini 5: A Leap Forward in Drone Technology
20481 kez okundu
 2
xAI’s Grok Chatbot Introduces Memory Feature to Rival ChatGPT and Google Gemini
14451 kez okundu
2
xAI’s Grok Chatbot Introduces Memory Feature to Rival ChatGPT and Google Gemini
14451 kez okundu
 3
7 Essential Foods for Optimal Brain Health
13256 kez okundu
3
7 Essential Foods for Optimal Brain Health
13256 kez okundu
 4
Elon Musk’s Father: “Admiring Putin is Only Natural”
13094 kez okundu
4
Elon Musk’s Father: “Admiring Putin is Only Natural”
13094 kez okundu
 5
Minnesota’s Proposed Lifeline Auto Insurance Program
10979 kez okundu
5
Minnesota’s Proposed Lifeline Auto Insurance Program
10979 kez okundu
Sigorta Güncel Sigorta Şikayet Güvence Haber Hasar Onarım Insurance News Ajans Sigorta Sigorta Kampanya Sigorta Ajansı Sigorta Sondakika Insurance News